Industrial Insights
Industrial Insights
- Details
- Sania Aziz
- Industrial Insights
- Date: 15th December 2025
- Year: 2025
AkzoNobel’s protective coatings brand, International, officially unveiled Chartek 2218E, the latest evolution of its renowned epoxy passive fire protection (PFP) solution, at ADIPEC 2025 in Abu Dhabi.
Building on over 50 years of innovation within the Chartek range, Chartek 2218E combines trusted protection with enhanced efficiency and performance. The coating sets a new standard in hydrocarbon pool fire protection, achieving a 2-hour rating in a single-coat application over Charlok mesh. Designed specifically for shop-applied steel, the boron-free epoxy intumescent offers the industry’s lowest UL1709-certified thickness and weight for a W10x49 steel section.
The streamlined application process allows for faster project completion, lower energy use, and reduced risk of delays while maintaining strict safety and environmental standards. Chartek 2218E reduces application hours by up to 50%, cuts shop-applied costs by up to 25%, and decreases material usage by a similar margin, delivering efficiency gains for fabricators and applicators. Its durability, corrosion resistance, and reduced energy demand contribute to sustainability goals and improved total cost of ownership, supporting AkzoNobel’s ambition to halve emissions across its value chain.
Customers can rely on Chartek 2218E’s technology platforms, which have demonstrated proven performance in real-world conditions. The coating provides UL 1709 120-minute pool fire protection, has been tested against ASTM D5894, and certified to UL2431, all without a prescribed topcoat. This ensures fire performance even after weathering and offers the flexibility to add a cosmetic topcoat without affecting long-term protection.
Launching at ADIPEC, one of the world’s most significant energy events, offered an ideal platform to demonstrate Chartek 2218E’s performance and efficiency. Attendees had the opportunity to view product samples and engage with experts, while a dedicated dinner on 5th November featured a presentation highlighting the coating’s value to projects.
Robin Wade, Global Fire Protection Manager at AkzoNobel, said, “Chartek 2218E represents the latest innovation in passive fire protection for the large two-hour pool fire market, which is critical for many oil and gas assets. Developed at our UKAS-accredited PFP facility in Felling, it reflects our continued commitment to investing in innovation and sustainability in structural fire protection. Chartek 2218E can be applied in a single coat with Charlok mesh, maximizing productivity without compromising robustness and durability. Its patented polysiloxane-modified epoxy technology means steelwork can be stacked with minimal damage, enhancing throughput and overall fire efficiency.”
Andy Holt, Business Development Manager for AkzoNobel Middle East, added, “Feedback from customers highlights that productivity and workshop efficiency remain some of the biggest challenges in oil and gas construction, and that’s exactly where Chartek 2218E delivers. Early demonstrations have been met with strong confidence from applicators and fabricators alike, who see the benefits first-hand in speed, consistency and ease of application. Maintaining that close collaboration with our customers is what drives continuous improvement and long-term trust.”
- Details
- Sania Aziz
- Industrial Insights
- Date: 13th November 2025
- Year: 2025
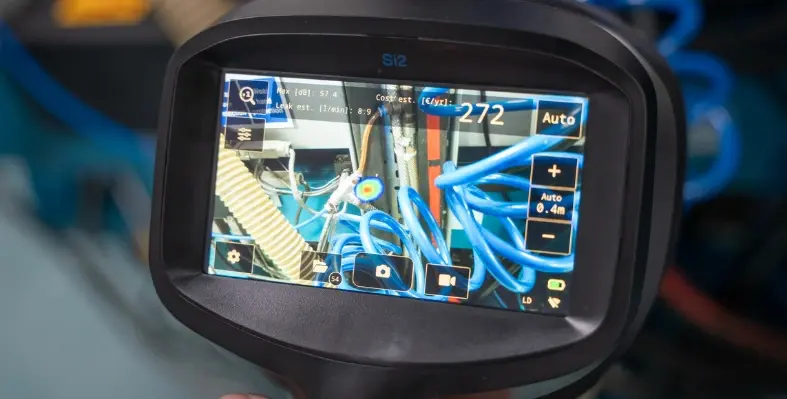
Flir’s acoustic imaging technology enables manufacturers to detect and repair leaks quickly, turning hidden losses into measurable energy savings and stronger safety performance throughout production.
Valued at more than US$120bn annually, the global glass industry has undergone profound change over the past 50 years. In the early 1970s, traditional sheet and plate glass methods dominated. By the mid-1970s, the rise of float glass across Europe, North America, and Japan revolutionised production, delivering better surface quality, lower costs, and the ability to manufacture larger panes that shaped modern architectural design.
By the 1980s and 1990s, the industry expanded into higher-performance products. Coated and insulated glass units emerged as demand for energy-efficient buildings grew. Low-emissivity coatings helped reduce solar heat gain without sacrificing transparency, paving the way for today’s energy-saving glass. Alongside this, manufacturers began modernising their operations. From the early 2000s onwards, automation, robotics, and digital controls dramatically improved consistency, reduced waste, and enabled real-time quality monitoring across production lines.
Acoustic imaging: fast, accurate leak detection
Amid these advancements, one essential resource is often overlooked, air. Compressed air powers actuators, pneumatic conveyors, tooling, and mould purging, making it indispensable yet costly. Even minor leaks can drain energy, reduce line pressure, and affect product quality. A single 3 mm leak at 6 bar running for 8,000 hours a year can cost around €2,800. Despite the industry’s progress in energy conservation, many facilities still use fossil-fuelled compressors only for that air to escape unnoticed.
The Flir Si2-LD can detect more than just compressed air. Its embedded software identifies and quantifies leaks of oxygen, nitrogen, ammonia, and other industrial gases.
In large production sites, leaks are often hidden and difficult to pinpoint. Fixing them is straightforward; finding them is not.
Flir, a global leader in thermal and acoustic imaging, has made the process far simpler. The handheld Si2-LD acoustic camera uses ultra-sensitive microphones to detect even the smallest gas or air leaks. Engineers can inspect equipment safely from a distance without interrupting production. Covering a wide frequency range from 2–130 kHz, the device ensures accurate detection in varied environments. Its powerful LED lights improve visibility in poorly lit areas, helping users quickly identify components and take action.
With Flir’s technology, manufacturers gain a practical, data-driven way to cut energy waste, enhance plant reliability, and improve safety across the entire operation.
- Details
- Sania Aziz
- Industrial Insights
- Date: 12th November 2025
- Year: 2025
flydubai has reaffirmed its commitment to safety excellence by signing the International Air Transport Association (IATA) Safety Leadership Charter, marking a major step in strengthening its organisational safety culture.
The charter was signed by flydubai’s CEO Ghaith Al Ghaith, and reflects the airline’s dedication to upholding the highest standards of safety across all areas of operation.
By joining more than 150 global airlines that have signed the charter, flydubai reinforces its commitment to fostering a proactive safety culture that prioritises the wellbeing of passengers and employees alike.
Developed in collaboration with industry stakeholders, the IATA Safety Leadership Charter is a global initiative designed to promote safety through visible leadership and engagement. It encourages aviation leaders to build trust, accountability, and continuous improvement across their organisations.
The charter’s principles focus on leading by example, fostering a culture of safety awareness, and driving ongoing evaluation and enhancement of safety practices at every level.
Ghaith Al Ghaith, chief executive officer at flydubai, said, “We are pleased to sign the IATA Safety Leadership Charter, re-emphasising our commitment to the highest standards of aviation safety. By embedding the Charter’s guiding principles into our daily operations and sharing our experiences, insights and best practices, we aim to further contribute towards a stronger and safer global aviation industry. Fostering a safety-first culture remains a high priority at flydubai and we look forward to working with our industry partners to maintain safety throughout our entire operations.”
Khalid Alhumaidan, senior vice president of compliance, safety & sustainability at flydubai, added, “Joining the IATA Safety Leadership Charter marks an important milestone in flydubai’s journey to continuously strengthen our safety culture. Leadership plays a vital role in shaping safety outcomes, and through this Charter, we reaffirm our commitment to promoting trust, accountability and transparency at every level of the organisation. It reflects our ongoing efforts to enhance our Safety Management System and ensure that every decision we make prioritises the wellbeing of our passengers, workforce and stakeholders.”
- Details
- Sania Aziz
- Industrial Insights
- Date: 11th November 2025
- Year: 2025
QatarEnergy LNG hosted its first-ever CEO HSEQ Excellence Awards at its Doha headquarters, marking a key milestone in recognising outstanding achievements in Health, Safety, Environment, and Quality (HSEQ) across the organisation.
The ceremony also served as the official launch of Safety Week 2025, bringing together the Chief Executive Officer, the Management Leadership Team, senior executives, and shareholder representatives to honour teams whose efforts continue to strengthen QatarEnergy LNG’s world-class safety culture.
Recognising achievements from 2024, the company presented 28 awards across seven categories, highlighting initiatives that delivered measurable HSEQ improvements, demonstrated strong leadership, and advanced a culture of continuous improvement and operational excellence.
During the event, QatarEnergy LNG also unveiled the 'Our HSEQ Excellence Journey installation', which was an interactive exhibit showcasing the company’s major milestones, innovative projects, and collaborative efforts that have shaped its progress over the years.
In his remarks, chief executive officer Sheikh Khalid bin Khalifa Al-Thani reaffirmed that safety is a core element of the company’s culture and identity.“At QatarEnergy LNG, safety is the foundation of our company. It is the promise we make to every employee, every partner, and every family, that we will do everything in our power to protect lives, safeguard our assets, and preserve the environment entrusted to us,” he said.
As a highlight of Safety Week 2025, the inaugural awards underscored QatarEnergy LNG’s commitment to fostering a culture where safety, environmental stewardship, operational discipline, and project excellence are integral to every aspect of its operations.
- Details
- Sania Aziz
- Industrial Insights
- Date: 28 October, 2025
- Year: 2025
ITAC Safety, led by CEO Suresh Kumar, has emerged as a key player in the UAE’s health and safety training sector, offering accredited programmes that align with the nation’s stringent regulatory standards.
In this interview, Kumar discusses how ITAC is tackling industry challenges through innovations such as Visual Impact Training (VIT) and e-learning, while expanding its footprint to Abu Dhabi and developing new sustainability-focused courses to strengthen workplace safety culture across the region. Read on:
How has ITAC Safety positioned itself within the UAE’s growing health and safety training landscape?
As you know that the training and information to the employees is a prime responsibility of any employer about the job and job related hazards to be controlled. The beauty of this region is that the [UAE] government is deeply concerned about the health and safety training requirements such as first aid, fire fighting, working at heights, confined space and more.
ITAC has gained all the relevant accreditation and approvals to meet out the requirements along with the best quality of training with their competent team. Recently we have successfully implemented Visual Impact Training (VIT) with the relevant health and safety topics to make short and captured by the learners.
What are some of the most pressing occupational safety challenges you see organisations in the Middle East facing today?
Here the climate is a big concern, which may affect the workers significantly. Additionally, language barriers, project deadlines, cost and others. However, any barriers can be managed when we are looking at safety as a culture which is a visionary project of the local government and the employers. The service provider like ITAC will strongly believe and support / follow the same.
Technology is rapidly changing how professionals learn. How is ITAC incorporating these innovations?
Rightly said. That’s the reason ITAC Safety incorporates online/virtual platforms/e-learning platforms wherever there is a possibility. You can also check out our website itacelearning.com.
Looking ahead, what are ITAC Safety’s priorities for further developing its training and consultancy offerings in the region?
ITAC Safety is looking forward to developing more on the VIT, which is really welcoming by the participants and the management and it is achieving its aim. Additionally, rapidly building up learning modules to create more awareness to the workers as short courses. ITAC Safety stepped into Abu Dhabi as well in September 2025, and additionally, we have started to develop the sustainability courses and consultancy services as well.
What key message do you plan to highlight during HSE MENA 2025?
Globally, people's awareness and understanding about their tasks will be helpful in reducing accidents and avoiding shortcuts. This will enable more proactive inputs to increase efficiency, revenue and quality output. We request all employers to plan and execute proper training, awareness and information through multiple channels to their employees. We at ITAC feel rather proud as we are part of a sector where we get to save lives, properties and the environment.
More details can be found on the ITAC Safety website.
- Details
- Sania Aziz
- Industrial Insights
- Date: 10th November 2025
- Year: 2025
As part of the Ministry of Petroleum and Mineral Resources’ (MoPMR) ongoing commitment to enhancing occupational safety, health, and environmental performance across Egypt’s energy sector, Yassin Mohamed, First Undersecretary of the Ministry and Supervisor of Environment, Safety and Health, Energy Efficiency, and Climate, conducted an inspection visit to Misr Fertilizers Production Company (MOPCO) in Damietta Governorate.
During the visit, Ahmed Mahmoud, Chairman of MOPCO, provided an overview of the company’s core operations, emphasising efforts to cultivate a safety-focused culture, strengthen risk management, and maintain compliance with environmental regulations.
The discussions also highlighted initiatives aimed at improving energy efficiency, reducing emissions, and boosting operational performance in alignment with international standards for the fertiliser and petrochemical industries.
Mohamed was briefed on MOPCO’s green production projects, including the Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) project, designed to capture 140,000 tons of CO₂ annually to enhance urea fertiliser output.
The visit also covered the green ammonia project, developed in partnership with Egypt’s leading solar developer, Scatec, which aims to produce 150,000 tons per year of ammonia using renewable energy and green hydrogen.
The inspection included tours of the company’s ammonia and urea production units, the main control centre, and ISO/IEC 17025-certified chemical laboratories that ensure rigorous quality control and reliable calibration results.
A field simulation of an ammonia gas leak was conducted to evaluate emergency preparedness. The drill demonstrated MOPCO’s strong response capabilities, using advanced equipment and fire trucks to contain the simulated leak and execute a high-altitude rescue operation, underscoring the proficiency and readiness of the company’s safety and emergency teams.
This visit follows Mohamed’s September inspection of Methanex Egypt’s factory in Damietta, where he assessed operational processes, control and prevention measures, and the effectiveness of the company’s safety systems. These visits reflect MoPMR’s proactive approach to fostering safety, sustainability, and innovation across Egypt’s energy and chemical industries.
- Details
- Sania Aziz
- Industrial Insights
- Date: 12th December 2025
Twiceme has partnered with Simpson, the iconic American helmet brand, to bring its digital safety technology to the motorcycle industry for the first time.
Unveiled at EICMA 2025 in Milan, the inaugural Twiceme-equipped Simpson helmets introduce a new level of rider protection. Integrated NFC technology allows instant access to vital medical and emergency information for riders and first responders.
Through the Twiceme app, users can leverage smart safety features including Medical ID, Emergency Services, Share Location, Get Back Timer, and Immobility Alert, giving riders greater control over their safety.
“We’re very excited to bring this technology into our helmets and to the motorcycle industry. Just like our founder, Bill Simpson, we never want to rest on what we’ve done. Our goal is to keep evolving — to bring riders the latest innovations and deliver the safest equipment possible,” said Jamie Beckett, director of motorcycle, Simpson.
“Partnering with Simpson marks an exciting step for Twiceme as we enter the US motorcycle market for the first time. By combining Simpson’s decades of helmet innovation with our smart safety technology, we’re introducing a new standard of protection for one of the world’s most passionate riding communities,” said Christian Connolly, CEO, Twiceme.
- Details
- Sania Aziz
- Industrial Insights
- Date: 12th December 2025
The global industrial safety helmets market, valued at US$4.83bn in 2024, is projected to reach approximately US$8.2bn by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.9% between 2025 and 2035.
Historical trends from 2019 to 2023 reveal steady growth, driven by expanding construction activities, manufacturing output, and intensified efforts to reduce workplace injuries across developed and emerging economies.
Industrial safety helmets, once basic hardhats, have evolved into advanced protective systems designed to safeguard workers from head injuries in high-risk environments such as construction sites, factories, and mining operations. This evolution has been shaped by the adoption of global safety standards including those from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). As compliance requirements become more stringent, demand for certified, ergonomic, and durable helmets continues to grow across sectors.
A key driver of this market expansion is the heightened awareness of workplace safety and the economic importance of injury prevention. Governments, particularly in regions with industrial expansion, have intensified safety mandates requiring the use of personal protective equipment (PPE). This has led enterprises to invest in high-quality helmets that combine safety, comfort, and durability. Technological advancements have also played a crucial role, with manufacturers incorporating innovative materials such as fibreglass, carbon fibre, and high-density polyethylene to produce helmets that are lighter yet stronger.
Another emerging trend is the increasing investment in smart helmets equipped with integrated sensors, GPS tracking, and real-time communication tools. These features enable proactive monitoring of workers’ safety conditions, helping reduce accident risks and improving emergency response times. Such innovations are expected to significantly influence market dynamics over the next decade as industries shift towards digital and connected safety ecosystems.
Regional insights
Regionally, the industrial safety helmets market exhibits diverse patterns of growth. In North America, the market benefits from robust occupational safety regulations and early adoption of smart protective devices. Europe remains a hub for innovation, focusing on composite material technologies and sustainable production practices. Countries like Germany and the United Kingdom are leading exporters of advanced safety gear and continue to invest heavily in research and development.
The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, however, represents the fastest-growing market. Massive urbanisation, large-scale construction projects, and rapid industrialisation in China, India, and Southeast Asia are fuelling unprecedented demand for protective equipment. Meanwhile, South America is witnessing a steady rise in safety gear adoption, supported by growing investments in the mining and infrastructure sectors.
In the Middle East and Africa (MEA), demand is being sustained by ongoing oil, gas, and construction projects across the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations and expanding industrial activity in African economies. As regional governments strengthen workplace safety legislation, helmet manufacturers are seizing opportunities to expand local partnerships and production facilities.
Overall, the industrial safety helmets market is entering a phase of technological innovation and regulatory maturity. With the convergence of digitalisation, sustainability, and safety compliance, the next decade will see a shift from traditional protective gear to intelligent, performance-optimised solutions that not only protect workers but also enhance operational efficiency across industries worldwide.
- Details
- Sania Aziz
- Industrial Insights
- Date: 12th December 2025
- Year: 2025
The US$1mn Human Energy Health and Wellbeing Awards, which aim to acknowledge and celebrate innovative, measurable solutions that enhance the physical and mental health of energy workers worldwide, will take centre stage at ADIPEC 2025, taking place from 3-6 November in Abu Dhabi.
Reflecting the UAE’s ongoing efforts to promote innovation, wellbeing, and ESG excellence, the Human Energy Awards are closely aligned with the UAE’s National Strategy for Wellbeing 2031 and the ‘We the UAE 2031’ Vision, which positions the country as a global leader in quality of life by fostering healthy lifestyles and promoting mental wellness.
The award will honour one organisation in the energy sector during ADIPEC 2025, with entries reviewed by an international jury of distinguished experts.
Initiated by Response Plus Holding PJSC (RPM), the leading pre-hospital care and emergency medical services provider in the Middle East, and Burjeel Holdings, a leading super-speciality healthcare provider in MENA, and supported by Prometheus Medical International, a UK-based defence medicine training company, the awards are the first of their kind in the energy sector.
The awards form the centrepiece of RPM’s participation at ADIPEC this year, reinforcing its role as the preferred medical partner for the global energy industry and underscoring its commitment to advancing healthcare provision, innovation, and employee wellbeing across the energy value chain.
Additionally, RPM subsidiary Prometheus Medical International will launch a one-of-a-kind global medical and security assurance programme for VIP travellers during ADIPEC. Prometheus will also showcase its comprehensive Mental Health and Employee Wellbeing Programme, an initiative dedicated to promoting psychological safety, enhancing workforce productivity, and reducing turnover by embedding mental health support.
Dr Rohil Raghavan, CEO of Response Plus Holding PJSC, said, “Our participation at ADIPEC 2025 is a strategic step in our journey to transform health and wellbeing standards across the global energy sector. The US$1mn Human Energy Award is designed to recognise and inspire organisations who think differently about health and wellbeing. As the industry evolves, we are committed to delivering world-class medical services, AI-driven innovations, and mental health programmes that empower organisations to protect their most valuable asset – their people.”
During the exhibition, RPM will also showcase state-of-the-art artificial intelligence solutions designed to enhance occupational health services tailored specifically for the energy industry. These technologies aim to improve early detection, prevention, and management of health risks in high-demand work environments.
- Details
- Sania Aziz
- Industrial Insights
- Date: 12th December 2025
Across industries worldwide, workers rely on the quality, fit, and performance of personal protective equipment (PPE) to stay safe on the job. Since hazards rarely occur in isolation, employees often need to wear multiple types of PPE simultaneously.
As a global leader in protective equipment, 3M continues to innovate solutions and will showcase its leading products at the A+A 2025 trade fair, taking place from 4-7 November in Düsseldorf.
According to 3M, the event allows it to demonstrate how its technologies and services work together to encourage consistent PPE use while addressing communication, comfort, fit, and performance needs.
Among the products on display are the 3M Speedglas Generation 5 Series Welding Helmet, offering advanced protection and customisable settings for versatile welders; the 3M PELTOR WS Alert XPV Headset, featuring solar-powered operation, Bluetooth MultiPoint technology, and noise-cancelling microphones for robust communication; the 3M DBI-SALA ExoFit XE Series Safety Harness, designed for comfort and safety at height; and the 3M Aura Particulate Respirator 9300+ Series, now upgraded with recycled materials and available in multiple protection levels.
3M also highlights its Integrated Protection Program, a holistic approach to PPE that combines technologies and services to promote consistent use and enhance worker safety. The programme underscores the value of PPE in protecting employees across industries, demonstrating how comprehensive health and safety strategies are strengthened through proper support resources.
Visitors to 3M’s booth will have the opportunity to engage with experts, explore interactive displays, and learn how selecting the right PPE for specific environments can improve workplace health and safety outcomes.
"At 3M, we are dedicated to advancing workplace safety through innovative solutions that enhance protection and productivity," said Aisha Barry, president, 3M’s Personal Safety Division. "At 3M, we’re changing the way we look at PPE and believe it works best when it works together, instead of getting in the worker’s way. Using PPE combinations that help enhance fit, comfort, communication, and productivity, it’s more likely that workers will embrace and wear their PPE all shift long.”
- Details
- Sania Aziz
- Industrial Insights
- Date: 27 October, 2025
- Year: 2025
Intersec Saudi Arabia hosted a key session that examined critical lessons from major fire disasters, including the Grenfell Tower fire in London, the Ghost Ship warehouse fire in Oakland, California, and the Marco Polo high-rise fire in Honolulu, Hawaii. The discussion underscored the urgent need for international collaboration to strengthen global fire safety frameworks.
The session was led by Jim Pauley, President and Chief Executive Officer of the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), who emphasised that individuals, organisations and authorities must work collectively to address safety gaps and create more resilient communities.
In response to tragedies such as Grenfell, NFPA developed the ‘NFPA Fire and Life Safety Ecosystem’, a comprehensive model that identifies key components required for effective safety systems. These include an informed public, government responsibility, the use of current codes and referenced standards, investment in safety, a skilled workforce, code compliance, and preparedness and emergency response.
Explaining the concept, Pauley said, “The ecosystem is a framework that defines the elements necessary to create and maintain an effective safety environment. The interconnected components mean that the failure of a single element can compromise the entire system, resulting in deaths, injuries, and property loss.”
Established in 1896, NFPA is a global nonprofit organisation dedicated to reducing death, injury, and economic loss caused by fire, electrical and related hazards. The association delivers expertise through more than 300 consensus codes and standards, as well as through education, research, and advocacy.
“We live in an era of innovation, but innovation without safety is a risk we cannot afford. To do this work, and to do it well, we have to see what’s coming, and we have to remember what came before,” Pauley added.
He also linked the discussion to Saudi Vision 2030, describing it as “a bold and ambitious plan to transform the Kingdom's economy and to elevate its global stature.” He noted that achieving this vision required world-class infrastructure built on robust safety standards.
The NFPA day at Intersec Saudi Arabia, curated by NFPA and chaired by Zahi Daher, NFPA’s Country Manager in Saudi Arabia, brought together key stakeholders from government and industry to explore innovative ways to enhance fire and life safety in support of Vision 2030.
- Details
- Sania Aziz
- Industrial Insights
- Date: 24 October, 2025
- Year: 2025
The growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the associated fire risks were discussed at the Fire Protection & Technology Summit at Intersec Saudi Arabia by Mike Brunzell, Vice President of Global Business Development at the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA).
Research from the International Energy Agency (IEA) indicated that global EV sales surpassed 17 million in 2024, representing more than 20% of total vehicle sales. As EV adoption accelerated, new and complex fire risks emerged, particularly in densely populated areas such as residential and commercial parking facilities.
Brunzell explained, “One of the major concerns we face is the risk of thermal runaway in lithium-ion batteries. While the data shows us that EV fires occur less frequently than fires in gas or diesel-powered vehicles, the research also shows that when they do occur, they can present unique and difficult challenges including longer burn durations, high heat release, toxic gases, re-ignition risks and significant water demand for suppression.”
Through the NFPA’s Fire Protection Research Foundation, extensive studies had been conducted into vehicle fire dynamics, suppression methods and ventilation system design. The findings showed that modern vehicles contained a significantly higher percentage of plastic (rising from less than 3% of total vehicle weight in the 1970s to nearly 10% today) creating greater combustible fuel loads. The increasing use of electronic components and intricate wiring systems had also introduced additional ignition hazards.
Brunzell underscored the critical need for safety regulations to evolve alongside advancing technology. “It is through the development of our codes and standards, research initiatives and training programmes that NFPA is proactively working to provide the guidance and the resources needed by fire protection professionals, property owners and policymakers to ensure the integration of EV infrastructure safety strategies,” he said.
The discussion highlighted that as EV adoption continued to expand globally, updating fire protection measures, codes and emergency response strategies would remain essential to mitigating emerging risks in the electric mobility era.