North America
North America
- Topic: HSE
- Region: North America
- Date: 4 September 2025
- Year: 2025
Two strategic partnerships with MEJA Construction hope to instil a stronger attitude towards health and safety on two projects in Henry and Clayton counties in Georgia
The construction projects include the demolition of two school gymnasiums and the construction of their replacements, and the construction of a premises encompassing a kitchen & cafeteria, gymnasium, media centre, classrooms and collaboration spaces.
OSHA will lead training around injury prevention and hazard exposure to workers set to take part in the projects, assist contractors in establishing health and safety management systems and conducting inspections, and monitor potential chemical risks.
The Georgia Institute of Technology On-site Safety and Health Consultation will also be involved in the partnership and projects in a stakeholder capacity.
OSHA's Strategic Partnership Program (OSPP) has been estimated to protect two million workers thus far.
- Topic: HSE
- Region: North America
- Date: 27 August 2025
- Year: 2025
The U.S. Department of Labor's Occupational Safety and Health Administration renewed its alliance with the National Waste & Recycling Association and the Solid Waste Association of North America with the aim of improving the safety and health of workers in the solid waste and recycling industry
Over the term of the three-year agreement, OSHA, NWRA and SWANA will focus on safety issues, including transportation hazards such as backovers and distracted driving, slips, trips and falls, as well as needlestick and musculoskeletal injuries. They will also address potential health issues associated with lithium battery hazards in waste and recycling collection and processing.
The participants will collaborate to develop resources such as educational articles, fact sheets, and toolkits aimed at preventing and mitigating hazards and will share information at industry conferences, forums and meetings. Particular attention will be paid small- and medium-sized employers, to ensure that all businesses within the waste and recycling industry have access to essential safety information and resources.
The initiative takes place under OSHA's Alliance Program, whereby the agency develops voluntary, collaborative working relationships with organisations committed to workplace safety and health. They include trade and professional associations, labour unions, educational institutions, community and faith-based groups, and government agencies.
Alliance participants work with OSHA to provide workers and employers with information, guidance, and resources to promote safety and health in workplaces in order to prevent workplace fatalities, injuries and illnesses. Alliances also ensure that workers know their rights and employers understand their responsibilities under the Occupational Safety and Health Act.
- Topic: HSE
- Region: North America
- Date: 21 August 2025
- Year: 2025
The US Department of the Interior is updating oil and gas commingling rules to align with the One Big Beautiful Bill Act.
'Commingling' means combining oil or gas production from two or more sources into a single stream for measurement and processing.
The updates, led by the Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement (BSEE), and the Bureau of Land Management (BLM), provide clear standards that support safe operations, improve efficiency and maximise recovery of America’s energy resources. BSEE has finalised a rule to clarify expectations for offshore commingling, ensuring production methods protect well integrity, safety and ultimate recovery. The BLM is also issuing interim guidance to broaden commingling authority on public and tribal lands until updated regulations are complete. Field offices are directed to process applications quickly and consistently under the One Big Beautiful Bill Act’s expanded provisions.
According to the Department of the Interior, these updates support the Trump administration’s energy and regulatory priorities by advancing the goals of Executive Order, “Unleashing American Energy.” which seeks to maximise the USA’s energy resources while reducing ‘burdensome and ideallocailly motivated” regulations which impede developemtn of these resources and put up costs. They also align with Secretary Burgum’s orders emphasizing safe, efficient and predictable oversight of oil and gas operations, reinforcing policies that remove unnecessary regulatory barriers while ensuring maximum resource recovery and environmental protection.
“From day one, the Trump administration has worked to cut red tape, strengthen America’s energy dominance and ensure responsible resource development,” said Secretary of the Interior Doug Burgum. “We’re delivering on that by aligning our regulations with the law, streamlining approval processes and giving operators a clear framework rooted in sound science and engineering. These updates make it easier to produce American energy without unnecessary bureaucratic hurdles, while at the same time protecting taxpayers, tribes and our shared energy future by ensuring production is safe, efficient and maximises the long-term value of our resources.”
- Date: 13 August 2025
- Year: 2025
The Voluntary Protection Programs Participants’ Association (VPPPA) has unveiled a new initiative aimed at helping companies enhance workplace safety and health performance.
Named the “Journey Toward Safety Excellence,” the programme was announced at the 2025 Safety+ Symposium in St. Louis in Missouri and provides organisations with a structured improvement plan.
The initiative offers a combination of self-assessments, mentoring, and customised guidance to support companies in strengthening their safety management systems. The programme is set to officially launch on 1 September.
Terry J. Schulte, Chairperson of VPPPA, explained that the initiative is designed to help employers achieve the performance standards seen at top-tier OSHA Voluntary Protection Program (VPP) sites.
To support this, the association has developed a free gap analysis tool that enables organisations to identify strengths and weaknesses within their existing safety and health practices. Participating companies can sign a letter of commitment and work alongside experienced mentors to create tailored improvement plans.
The launch of “Journey Toward Safety Excellence” follows OSHA’s announcement of its new “Pathways to Safety and Health Success” programme, which expands the core elements of VPP from four to seven and aligns them with OSHA’s recommended best practices.
Schulte noted that the VPPPA initiative is intended to complement OSHA’s programme, offering additional resources and support for companies striving to achieve excellence in workplace safety.
Established in 1985, VPPPA represents over 1,400 companies and worksites across the United States. The association promotes workplace health and safety through collaboration, mentorship, and educational programmes.
Further details about the “Journey Toward Safety Excellence” initiative are available on the official VPPPA website.
- Date: 8 August 2025
- Year: 2025
The U.S. Department of Labor’s Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is joining forces with businesses nationwide to celebrate Safe + Sound Week from 11-17 August 2025.
This annual campaign highlights the achievements of workplace safety and health programmes and provides valuable information to help keep workers safe across the country.
Safe + Sound Week encourages organisations to adopt effective safety measures that enable them to identify and manage workplace hazards proactively. By doing so, businesses can prevent injuries and illnesses, enhance overall sustainability, and improve their financial performance.
The 2025 event will focus particularly on emergency preparedness and response. Emergencies can occur unexpectedly anywhere and at any time, posing risks not only to workers but also to customers and the public.
Such incidents can disrupt operations, cause physical harm, or result in environmental damage.
During the week, OSHA will offer resources aimed at helping businesses stay informed about potential risks, develop robust emergency action plans, and prepare employees to respond quickly and effectively if an emergency arises.
These tools are designed to support organisations in building resilience and protecting their workforce.
Safe + Sound Week is open to all organisations regardless of their size or industry sector. Participation demonstrates a company’s dedication to workplace safety and provides an opportunity to strengthen existing safety and health programmes.
Last year, over 5,000 businesses took part in Safe + Sound Week, working together to raise awareness of the importance of safety in the workplace.
The initiative continues to grow each year, reflecting a shared commitment to creating safer and healthier work environments across the United States.
- Topic: HSE
- Region: North America
- Date: August 7th
- Year: 2025
A two-day workshop launched the Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement (BSEE)'s new 'Dominance by Design' initiative, which unites experts and government representatives to develop future offshore resource strategy.
The workshop was held at the BSEE's Gulf of America regional office, and was described as "a unique opportunity to engage directly with the experts who operate in the field every day... this engagement has provided BSEE with invaluable insights to ensure our oversight is not just robust, but also agile and efficient," by the bureau's assistant director Seong Kim.
Evan Zimmerman, the Offshore Operators Committee's executive director, praised the new initiative.
"This session was highly valuable, providing a constructive platform to identify and address challenges in our offshore energy permitting processes.
"By focusing on the permit-related data, we can take a practical approach to improving efficiency and streamlining pathways for important offshore energy projects, supporting American energy goals."
The BSEE has confirmed plans to hold additional 'Dominance by Design' sessions to ensure a smart and strategic approach to developing the offshore energy sector.
- Date: 28 July 2025
- Year: 2025
Honeywell has been selected to upgrade the fire alarm system at Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport’s Terminal 4, the busiest terminal at the airport with over 80 gates across eight concourses.
The project will replace the original 2003 Honeywell system with advanced fire safety technology that meets the latest UL standards.
As part of the upgrade, new automated devices and enhanced system modules will improve emergency response and operational efficiency.
A digital dashboard will provide real-time insights, helping to cut maintenance costs and reduce manpower amid ongoing labour shortages.
Updated maps through Honeywell’s Enterprise Buildings Integrator (EBI) platform will also improve alarm visualisation and guide emergency responders more accurately.
The project is scheduled for completion in 2026 and will ensure full protection for the terminal, which serves nearly 94,000 passengers daily, throughout the process.
The project highlights Honeywell’s role in delivering safety-critical infrastructure upgrades while supporting broader megatrends in automation, aviation, and the energy transition.
“This award to enhance the Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport's fire alarm system reflects our commitment to delivering innovative and reliable automation solutions that protect this busy airport while also helping ensure uninterrupted operations for passengers and staff,” Sudhakar Janakiraman, president, Honeywell Building Solutions.
“We are honored to work on this vital safety initiative that builds on a long-standing and valued relationship.”
- Date: 24 July 2025
- Year: 2025
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has announced that it will offer free and confidential black lung screenings for coal miners throughout July and August 2025.
This mobile screening initiative is designed to help detect coal workers’ pneumoconiosis, commonly known as black lung disease, at an early stage.
The disease is a serious but preventable occupational condition caused by prolonged exposure to coal mine dust.
To ensure easy access, NIOSH will deploy a mobile testing unit across various communities and mine sites in Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Maryland.
The programme is open to all coal miners, including current and former workers from underground, surface, and contract mining operations.
Participants will receive a private lung health report at no cost. All results will remain confidential and are protected under federal law.
The screening process takes approximately 30 minutes and includes a work and respiratory history, chest x-ray, blood pressure check, and a breathing test (spirometry).
While walk-ins are welcome, miners are encouraged to schedule an appointment. Test results are generally sent to participants within 8-10 weeks.
In West Virginia, screenings will take place at the NMRA Post 5 Mine Rescue Contest at Mylan Park, Morgantown, from 29-31 July, between 8:00 a.m. and 4:30 p.m.
Another session will be held at Price Cutter in Mannington on Tuesday, 5 August, from 8:00 a.m. to 3:30 p.m.
In Maryland, screenings are scheduled for Wednesday, 27 August, at the Grantsville Volunteer Fire Department from 8:00 a.m. to 3:30 p.m.
NIOSH completed its screenings in Pennsylvania at Greene County Fairgrounds in Waynesburg on 16 and 17 July.
- Topic: HSE
- Region: North America
- Date: 23 July 2025
- Year: 2025
The U.S. Department of Labor has updated its policy on penalty and debt collection procedures with the aim of minimising the burden on small businesses and encouraging prompt action to address hazards
The new policy, outlined in the Penalties and Debt Collection section of OSHA’s Field Operations Manual, increases penalty reductions for small employers, making it easier for small businesses to invest resources in compliance and hazard abatement. For example, a penalty reduction level of 70%, which was previously only applicable for businesses with 10 or fewer employees, will now be extended to include businesses who employ up to 25 employees. The revisions also include new guidelines for a 15% penalty reduction for employers who immediately take steps to address or correct a hazard.
Additionally, the updated policy expands the penalty reduction for employers without a history of serious, willful, repeat, or failure-to-abate OSHA violations. Under OSHA’s revised policy, employers who have never been inspected by federal OSHA or an OSHA State Plan, as well as employers who have been inspected in the previous five years and had no serious, willful, or failure-to-abate violations, are eligible for a 20% penalty reduction.
The new policies are effective immediately, and investigations in which penalties have not yet been issued are covered by the new guidance.
OSHA retains the right to withhold penalty reductions where they do not advance the goals of the Occupational Safety and Health Act.
"All employers should be offered the opportunity to comply with regulations that help maintain a safe working environment,” said deputy secretary of Labor Keith Sonderling. “Small employers who are working in good faith to comply with complex federal laws should not face the same penalties as large employers with abundant resources. By lowering penalties on small employers, we are supporting the entrepreneurs that drive our economy and giving them the tools they need to keep our workers safe and healthy on the job while keeping them accountable."
- Date: 22 July 2025
- Year: 2025
Angeles Equity Partners, a private investment firm focused on niche manufacturing, critical industrial services and specialty distribution businesses, and Kain Capital, a private equity firm investing in healthcare services and technology, have announced the merger of Agile Occupational Medicine and Akeso Occupational Health.
This strategic combination creates the second-largest independent occupational medicine provider in the United States, with 42 locations across California and Arizona.
By combining two high-performing platforms with complementary clinic networks, the merger aims to strengthen the delivery of high-quality, efficient care focused on improving patient outcomes and helping employers return injured workers to health and productivity.
Both Agile and Akeso are leaders in occupational medicine, a discipline dedicated to preventing, diagnosing and managing work-related injuries and illnesses.
Their combined offerings now include a wide range of clinical services, from work injury treatment to ancillary services such as physical therapy, chiropractic care and acupuncture.
The new entity also provides comprehensive employer-focused solutions, including drug and alcohol screening, regulatory and pre-employment physicals, and hazardous material evaluations.
The merger is designed to expand access to care, enhance service offerings and streamline operations through innovation and a unified commitment to quality.
With an integrated platform and a shared vision, Agile and Akeso aim to be a trusted healthcare partner for employers while ensuring that injured employees receive prompt, expert treatment and are supported throughout their recovery journey.
“Combining Agile and Akeso strengthens our mission of providing timely, effective, and differentiated care to the workers we serve,” said Frank Spelman, managing director at Angeles Equity Partners and board member of Agile. “This merger puts us at the forefront of California’s occupational medicine segment, with the medical expertise, operational breadth, and geographic coverage required to deliver a full suite of healthcare services to, and superior outcomes for, statewide employers.”
“Employers need a reliable healthcare partner who can scale with their needs, and this merger delivers on that promise,” said Kunal Kain, managing partner at Kain Capital and chair of the board of Akeso. “With our combined footprint, we can now provide employers broader access to high-quality, flexible care options.”
“I’m excited to work alongside Dr. Yadidi and the talented team at Akeso,” said Dr. Minh Nguyen, chief medical officer of Agile. “Both organisations are committed to raising the standard of care for injured workers and improving their outcomes with faster recovery times and more efficient service.”
“This partnership strengthens our ability to care for injured workers throughout the state,” said Dr. Kayvon Yadidi, chief medical officer of Akeso. “I’m looking forward to partnering with Dr. Nguyen and combining our expertise to improve care and support for both employees and employers.”
- Date: 10 July, 2025
- Year: 2025
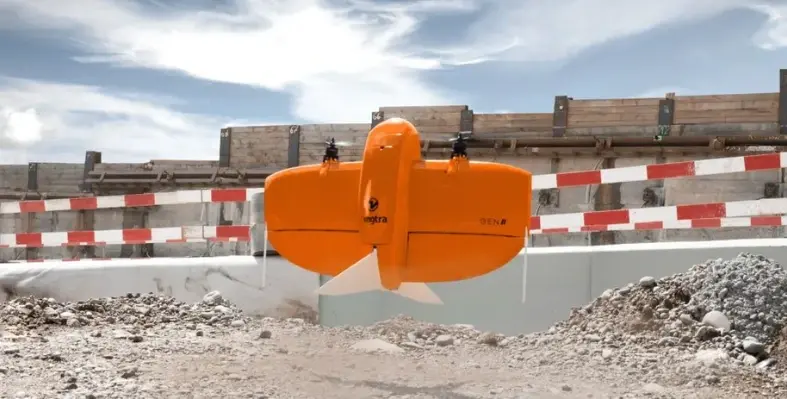
CSA Ocean Sciences Inc. (CSA), a global marine environmental consultancy, has enhanced its disaster response capabilities with the addition of the WingtraOne GEN II unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) to its uncrewed systems fleet.
Designed for rapid post-disaster assessments, the new UAV complements CSA’s existing suite of uncrewed surface vehicles (USVs), enabling the firm to efficiently evaluate storm-impacted infrastructure across inland, coastal, and offshore locations.
The WingtraOne GEN II features vertical take-off and landing (VTOL), allowing it to operate in confined or debris-covered areas. Capable of surveying up to 310 hectares in under 50 minutes, the UAV significantly accelerates damage assessment timelines. With an IP54 rating and resilience in sustained winds up to 27 mph, the platform supports various payloads, including RGB, LiDAR, and multispectral sensors, tailored to the assessment’s scope.
This airborne capability complements CSA’s SeaRobotics-built USV fleet, which includes 1.8-m to 11.0-m vessels equipped with modular sensor arrays for hydrographic mapping, submerged debris detection, and waterway navigability assessment, especially in conditions hazardous to crewed operations.
In anticipation of heightened tropical activity in the Atlantic Basin, CSA is actively coordinating with FEMA, state emergency agencies, utility providers, and insurers to prepare for rapid response. Its Crisis Management Team offers a 24/7 hotline for clients and partners, enabling immediate incident registration and deployment of tailored response teams.
“In the critical hours following hurricanes, floods, and other natural disasters, rapid situational awareness is essential,” said Chris Echols, CSA’s vice president of commercial operations and Geomatics Lead. “By deploying autonomous craft rather than personnel in potentially hazardous environments, we can safely and efficiently deliver precise images and data from above, on, and below the water that allow response teams to prioritise the most appropriate action plan. Our latest acquisition, the WingtraOne GEN II UAV, brings a new dynamic to our time-sensitive surveying capabilities, delivering high-resolution aerial maps, 3D models, and orthomosaics with ultra-precise accuracy—as tight as 1 cm with Post-Processed Kinematic (PKK).”
“Our mission is simple: to deliver clarity, speed, and safety when it matters most,” added Echols. “By integrating surface and subsurface data, CSA is now able to deliver an unparalleled understanding of the post-disaster landscape, enhancing decision-making for emergency managers, FEMA units, insurers, and infrastructure providers, all while keeping personnel out of harm’s way in often dangerous and unpredictable environments.
“All CSA’s disaster response technologies are engineered to minimise risk to personnel while accelerating the delivery of actionable insights. Whether scanning rooftops for insurance assessments, identifying structural collapse, or guaranteeing safe maritime navigation, CSA’s disaster response service is designed to optimise survey time, streamline overheads, and increase operational confidence.”
- Topic: Fire Safety
- Region: North America
- Date: 4 July 2025
- Year: 2025
‘Explosion, fire or burns’ was the leading cause of fatalities in the oil and gas sector in 2024, according to the International Association of Oil & Gas Producers' (IOGP) newly-published Safety Performance Indicators, which are based on data from its member companies
‘Explosion, fire or burns’ accounted for 41% of fatalities, with 13 fatalities in five separate incidents.
‘Struck by (not dropped object)’ accounted for 13% of fatalities, with four fatalities in four separate incidents. ‘Assault or violent act' also accounted for 13% of fatalities, with four fatalities in a single incident, while falls from height accounted for three fatalities.
According to the Safety Performance Indicators, there were 32 fatalities in 2024 occurring in 21 separate incidents. While all of these incidents were tragedies, it is nevertheless encouraging that the fatal accident rate (0.77) was 6% lower than last year’s figure (0.82), and has decreased by over 90% since 1985.
In terms of activity, the highest number of fatalities was recorded in 'Drilling, workover, well operations' (34%), with 11 fatalities as a result of six separate incidents.
The overall total recordable injury rate (TRIR) was 0.81, 4% lower than in 2023 (0.84), while the overall lost time injury rate (LTIR) (fatalities and lost work day cases per million work hours) was 0.24, unchanged compared with 2023.
Participating IOGP member companies reported 946 lost work day cases (LWDCs), 22% categorised as ‘Slips and trips’, 20% 'Caught in, under or between (excl. dropped objects)' and 16% ‘Struck by (not dropped object).
North America had a fatal accident rate of 0.93 compared with a global average of 0.77, and total recordable injury rate again relatively high at 1.62 compared with a global average of 0.81, while the LTIR was 0.28, near to the global average of 0.24.
North America fatalities
In North America there were seven fatalities in 2024, with 208 LWDCs. These reflect the predominance of the ‘explosion, fire or burns’ category as the cause of fatalities.
The fatalities were as follows:
- One contractor employee died as a result of a fire in a large-scale production operation onshore Mexico, where lack of communications between workers was cited as a factor;
- An employee of a subcontractor died as a result of a traffic collision, onshore USA;
- A contractor worker in an onshore USA operation died during the re-running of tubing into a well after repair, when the travelling block of the draw works struck them while being lowered to the rig floor. Not following correct procedures and the disabling or removal of guards, warning systems or safety devices were cited as factors;
- A worker was electrocuted during a flex line spooling operation, onshore USA, when a telehandler made contact with an overhead powerline. Inadequate initial emergency response and inadequate or incorrect use of equipment were cited as factors;
- Three contractors died as a result of a fire in a processing centre, offshore Mexico where there was a sudden loss of containment and release of gas in a high-pressure fuel gas heater, causing a fire and explosion. The fire spread due to the storage of hazardous chemicals located on the second and third levels of the platform and the poor coordination in emergency response. Lack of planning, failure in communications and inadequate maintenance/inspection/testing were cited as factors.
“The two most adopted IOGP Recommended Practices, the Life Saving Rules and Process Safety Fundamentals were developed based on analysis of the fatal accident data, and following these will help prevent future incidents,” said Steve Norton, IOGP Health, Safety, Security & Wells director. “At IOGP we continue to promote adoption of these practices and through the work of the Committees update and issue new Recommended Practices to address key gaps observed in the safety data.”
IOGP is currently developing new guidance for Process Safety in Design, Process Safety for Leaders, Guidelines for Determination of Process Safety Events that could result in Fatality and / or Permanent Impairment, and Process Safety Leading Indicators.
The Safety Performance Indicators are free to download from the IOGP website at https://www.iogp.org/bookstore/product-category/safety/